SpringCloudConfig 主要用于应用的配置热更新。本章主要介绍SpringCloudConfig的热更新原理
数据流
SpringCloudConfig 的 工作流程:
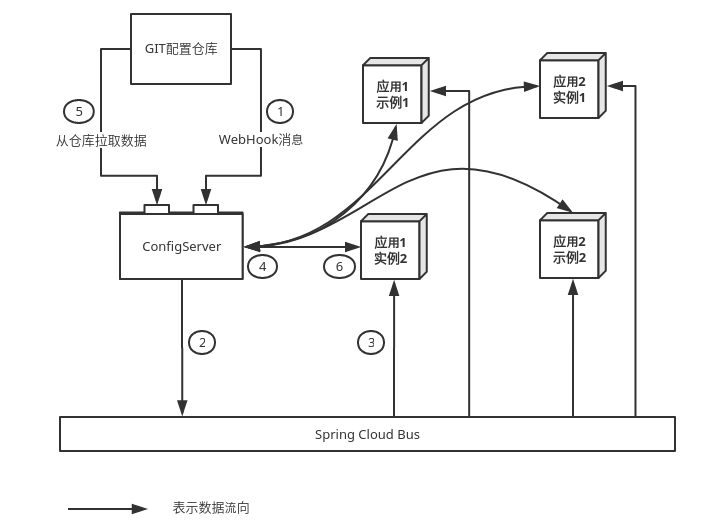
- 将修改的配置信息提交到Git,触发 WebHook。WebHook用 Http 的形式向 ConfigServer 发送 refresh 请求。
- ConfigServer 将这个消息发送给 spring cloud bus(用kafka或者rabbitMQ实现)
- 每个应用实例中有一个 config-client,将会收到这个 refresh 消息
- 如果 destination 和自己匹配,就执行刷新动作。 向 config-server 请求配置
- config-server 拉取配置仓库中的最新配置文件并转成相应的json格式
- 回传给 config-client,随后 config-client 将内容更新到上下文中。
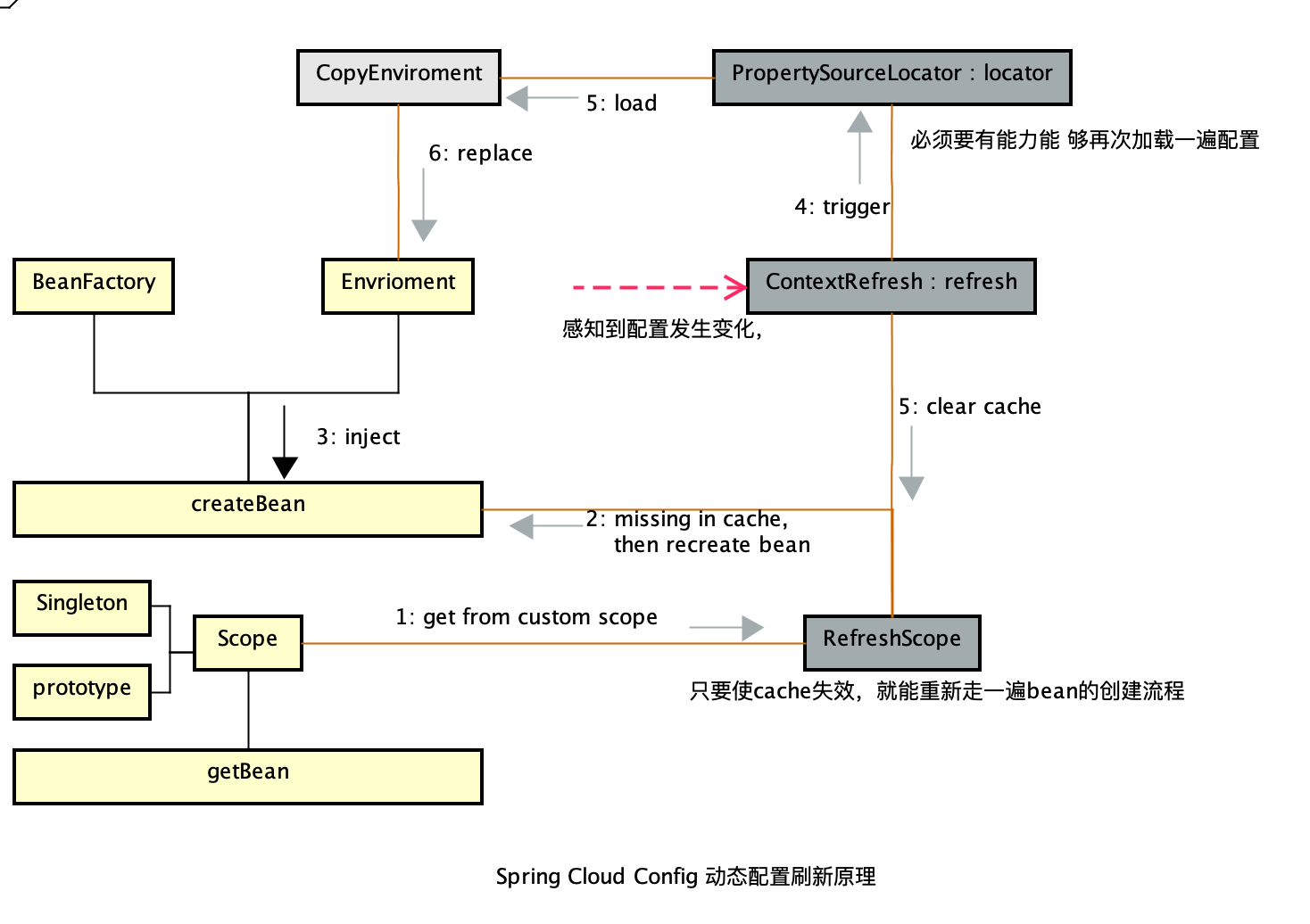
配置刷新原理
当触发热更新的时候,会调用 ContextRefresher 的 refresh()。方法的实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public synchronized Set<String> refresh() {
Set<String> keys = refreshEnvironment();
this.scope.refreshAll();
return keys;
}
public synchronized Set<String> refreshEnvironment() {
Map<String, Object> before = extract(
this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources());
addConfigFilesToEnvironment();
Set<String> keys = changes(before,
extract(this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources())).keySet();
this.context.publishEvent(new EnvironmentChangeEvent(this.context, keys));
return keys;
}
|
这个方法接收了环境中所有的 PropertySource ,并将其中的非标准属性源的所有属性汇总到一个 Map 。
这里的标准属性源如下所示:
- systemProperties
- systemEnvironment
- servletContextInitParams
- servletConfigInitParams
- configurationProperties
- jndiProperties
StandardEnvironment 会注册系统变量(System Properties)和环境变量(System Environment)
StandardServletEnvironment 会注册 Servlet 环境下的 Servlet Context 和 Servlet Config 的初始参数(Init Params)和JNDI 的属性。
###addConfigFilesToEnvironment方法
addConfigFilesToEnvironment() 的实现逻辑:
- 创建新的SpingBoot来获取新的属性源
- 对比新旧数据源: 1、将旧的数据源替换成新的数据源;2、将全新的数据源添加到 this.context.getEnvironment中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| ConfigurableApplicationContext addConfigFilesToEnvironment() {
ConfigurableApplicationContext capture = null;
try {
StandardEnvironment environment = copyEnvironment(
this.context.getEnvironment());
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder(Empty.class)
.bannerMode(Mode.OFF).web(WebApplicationType.NONE)
.environment(environment);
builder.application()
.setListeners(Arrays.asList(new BootstrapApplicationListener(),
new ConfigFileApplicationListener()));
capture = builder.run();
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(REFRESH_ARGS_PROPERTY_SOURCE)) {
environment.getPropertySources().remove(REFRESH_ARGS_PROPERTY_SOURCE);
}
MutablePropertySources target = this.context.getEnvironment()
.getPropertySources();
String targetName = null;
for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) {
String name = source.getName();
if (target.contains(name)) {
targetName = name;
}
if (!this.standardSources.contains(name)) {
if (target.contains(name)) {
target.replace(name, source);
}
else {
if (targetName != null) {
target.addAfter(targetName, source);
}
else {
target.addFirst(source);
targetName = name;
}
}
}
}
}
finally {
}
return capture;
}
|
###属性源更新后处理
- 通过
changes方法 收集发生改变的key集合。
- 通过
publishEvent方法 发送EnvironmentChangeEvent 事件
- 调用 RefreshScope.refreshAll 方法: 将refresh scope中的Bean 缓存失效,当再次从refresh scope中获取这个Bean时,发现取不到,就会重新触发一次Bean的初始化过程。
##EnvironmentChangeEvent
EnvironmentChangeEvent 主要触发两个行为:
- 重新绑定上下文中所有使用了
@ConfigurationProperties 注解的 Spring Bean。
- 如果
logging.level.* 配置发生了改变,重新设置日志级别。
这两段逻辑分别可以在 ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder 和 LoggingRebinder 中看到。
###ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder
ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder 类的监控方法onApplicationEvent 很简单,主要就是遍历每个 Bean,destroyBean和initializeBean每个bean。
需要注意的是: ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder的beans字段 只包含@ConfigurationProperties注解的Bean。因此配置的热更新只会影响 @ConfigurationProperties注解的Bean.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| @ManagedOperation
public void rebind() {
this.errors.clear();
for (String name : this.beans.getBeanNames()) {
rebind(name);
}
}
@ManagedOperation
public boolean rebind(String name) {
if (!this.beans.getBeanNames().contains(name)) {
return false;
}
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
try {
Object bean = this.applicationContext.getBean(name);
if (AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
bean = ProxyUtils.getTargetObject(bean);
}
if (bean != null) {
this.applicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()
.destroyBean(bean);
this.applicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()
.initializeBean(bean, name);
return true;
}
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
this.errors.put(name, e);
throw e;
}
catch (Exception e) {
this.errors.put(name, e);
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot rebind to " + name, e);
}
}
return false;
}
|
###LoggingRebinder
LoggingRebinder 的逻辑很简单,只是调用了 LoggingSystem 的方法重新设置了日志级别.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| @Override
public void onApplicationEvent(EnvironmentChangeEvent event) {
if (this.environment == null) {
return;
}
LoggingSystem system = LoggingSystem.get(LoggingSystem.class.getClassLoader());
setLogLevels(system, this.environment);
}
protected void setLogLevels(LoggingSystem system, Environment environment) {
Map<String, String> levels = Binder.get(environment)
.bind("logging.level", STRING_STRING_MAP)
.orElseGet(Collections::emptyMap);
for (Entry<String, String> entry : levels.entrySet()) {
setLogLevel(system, environment, entry.getKey(), entry.getValue().toString());
}
}
private void setLogLevel(LoggingSystem system, Environment environment, String name,
String level) {
try {
if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("root")) {
name = null;
}
level = environment.resolvePlaceholders(level);
system.setLogLevel(name, LogLevel.valueOf(level.toUpperCase()));
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Cannot set level: " + level + " for '" + name + "'");
}
}
|
##RefreshScope
1
2
3
4
5
| public void refreshAll() {
super.destroy();
this.context.publishEvent(new RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent());
}
|
RefreshScope 是用来存放 scope 类型为 refresh 类型的 Bean(即: 使用RefreshScope注解标识的Bean)。
当一个 Bean 既不是 singleton 也不是 prototype 时,就会从自定义的 Scope 中去获取 Bean ( Spring 允许自定义 Scope ),然后调用Scope的get方法来获取一个实例。
Spring Cloud 扩展了Scope,从而控制了整个 Bean 的生命周期。当配置需要动态刷新的时候, 调用this.scope.refreshAll()这个方法,就会将整个RefreshScope的缓存清空,完成配置可动态刷新的可能。
Scope 的相关介绍
数据源 种类
实践问题
需要在配置中心中添加 force-pull 信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| spring:
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
force-pull: true
|
参考
Spring Cloud 是如何实现热更新的
ppt

