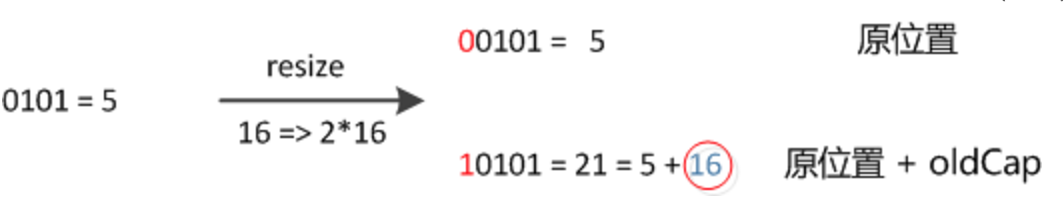[TOC]
关键点 基于map接口的非同步实现,不保证顺序,允许null key/value,默认大小16,按2倍扩增。
重要参数 threshold 代表的是一个阈值,通常小于数组的实际长度。这个阈值的具体值则由负载因子(loadFactor)和数组容量来决定。
threshold = capacity * loadFactor。
伴随着元素不断的被添加进数组,一旦数组中的元素数量达到这个threshold,那么表明数组应该被扩容而不应该继续任由元素加入。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int threshold;final float loadFactor;static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4 ;static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f ;static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30 ;
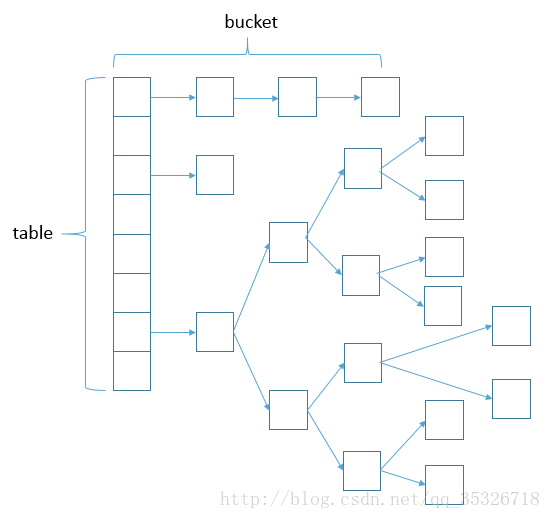
HashMap 数据结构 首先,HashMap 是 Map 的一个实现类,它代表的是一种键值对的数据存储形式。Key 不允许重复出现,Value 随意。jdk 8 之前,其内部是由数组+链表来实现的,而 jdk 8 对于链表长度超过 8 的链表将转储为红黑树。大致的数据存储形式如下:
主体为table数组结构,数组的每一项元素是一个链表。
下面的代码就是上述提到的数组,数组的元素都是 Node 类型,数组中的每个 Node 元素都是一个链表的头结点,通过它可以访问连接在其后面的所有结点。
1 transient Node<K,V>[] table;
Node<K,V> Node 是一个单向列表,她实现了 Map.Entry接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 static class Node <K ,V > implements Map .Entry <K ,V > final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this .hash = hash; this .key = key; this .value = value; this .next = next; } public final K getKey () return key; } public final V getValue () return value; } public final String toString () return key + "=" + value; } public final int hashCode () return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); } public final V setValue (V newValue) V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; } public final boolean equals (Object o) if (o == this ) return true ; if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue())) return true ; } return false ; } }
红黑树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 static final class TreeNode <K ,V > extends LinkedHashMap .Entry <K ,V > TreeNode<K,V> parent; TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; boolean red; TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { super (hash, key, val, next); } final TreeNode<K,V> root () for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this , p;;) { if ((p = r.parent) == null ) return r; r = p; } } }
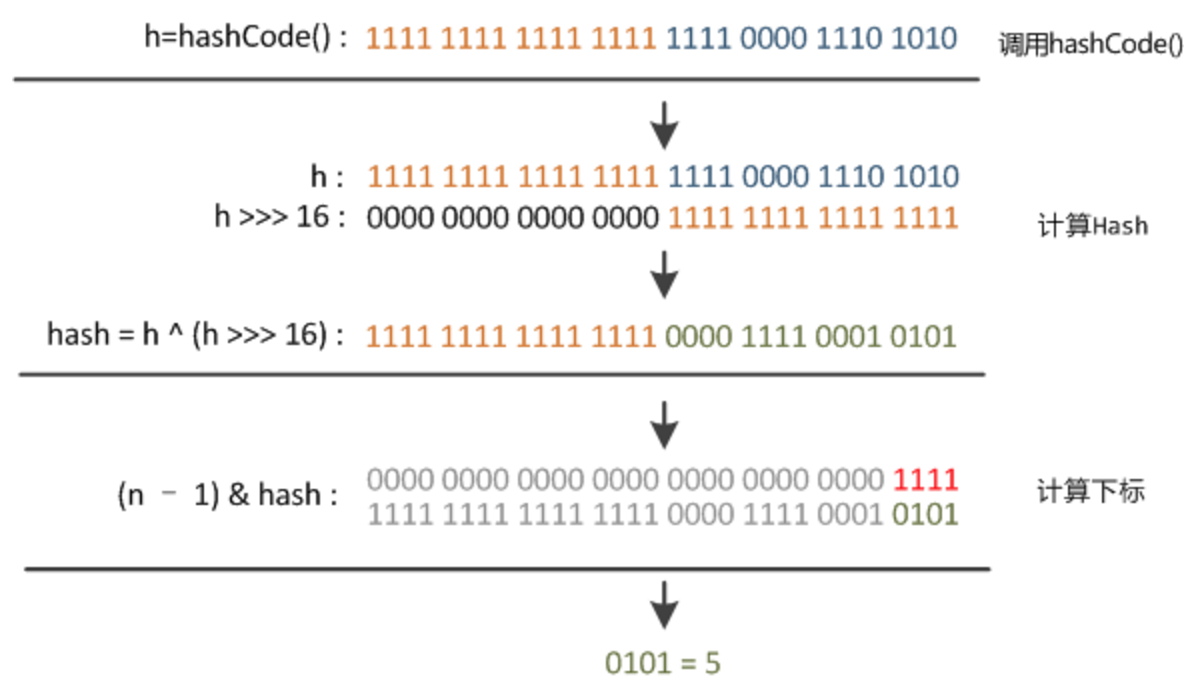
index 计算 1 2 3 4 static final int hash (Object key) int h; return (key == null ) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16 ); }
1 int index = (n - 1 ) & hash(key)
hash函数实现:高16bit不变,低16bit和高16bit做了一个异或
(n-1)&hash: n 表示table的大小,即是取hash的低(n-1)位作为index
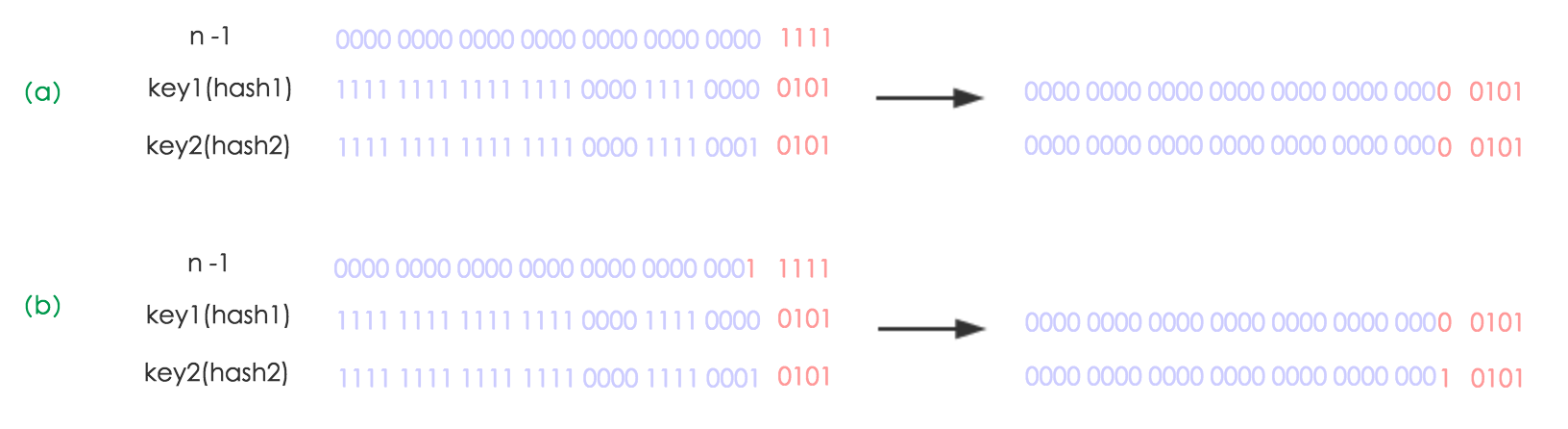
resize函数 resize 巧妙设计 由于 hashMap 使用的是2次幂的扩展(指长度扩为原来2倍),所以,元素的位置要么是在原位置,要么是在原位置再移动2次幂的位置。
图(a)表示扩容前的key1和key2两种key确定索引位置的示例,
图(b)表示扩容后key1和key2两种key确定索引位置的示例,
其中hash1是key1对应的哈希与高位运算结果。
元素在重新计算hash之后,因为n变为2倍,那么n-1的mask范围在高位多1bit(红色),因此新的index就会发生这样的变化:
因此,我们在扩充HashMap的时候,不需要重新计算hash,只需要看看原来的hash值新增的那个bit是1还是0就好了,是0的话索引没变,是1的话索引变成“原索引+oldCap”
源码 resize 函数实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 public class HashMap <K ,V > extends AbstractMap <K ,V > implements Map <K ,V >, Cloneable , Serializable { final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null ) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0 ; if (oldCap > 0 ) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1 ) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1 ; } else if (oldThr > 0 ) newCap = oldThr; else { newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int )(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0 ) { float ft = (float )newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float )MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int )ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings ({"rawtypes" ,"unchecked" }) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; table = newTab; if (oldTab != null ) { for (int j = 0 ; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null ) { oldTab[j] = null ; if (e.next == null ) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1 )] = e; else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this , newTab, j, oldCap); else { Node<K,V> loHead = null , loTail = null ; Node<K,V> hiHead = null , hiTail = null ; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0 ) { if (loTail == null ) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null ) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null ); if (loTail != null ) { loTail.next = null ; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null ) { hiTail.next = null ; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } return newTab; } }
put函数实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 public class HashMap <K ,V > extends AbstractMap <K ,V > implements Map <K ,V >, Cloneable , Serializable { public V put (K key, V value) return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false , true ); } final V putVal (int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1 ) & hash]) == null ) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null ); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this , tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0 ; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null ) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null ); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1 ) treeifyBin(tab, hash); break ; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break ; p = e; } } if (e != null ) { V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null ) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null ; } }
对key的hashCode()做hash,然后再计算 index;
如果index没碰撞直接放到table数组里;
如果碰撞了,以链表的形式接在数组中元素的后面 ;
如果碰撞导致链表过长(大于等于TREEIFY_THRESHOLD),就把链表转换成红黑树;
如果节点已经存在就替换old value(保证key的唯一性)
如果bucket满了(超过load factor*current capacity),就要resize。
get函数实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class HashMap <K ,V > extends AbstractMap <K ,V > implements Map <K ,V >, Cloneable , Serializable { public V get (Object key) Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; } final Node<K,V> getNode (int hash, Object key) Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1 ) & hash]) != null ) { if (first.hash == hash && ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null ) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null ); } } return null ; } }
table数组的第一个节点,直接命中;
如果有冲突,则通过key.equals(k)去查找对应的entry。
若为树,则在树中通过key.equals(k)查找,O(logn);
若为链表,则在链表中通过key.equals(k)查找,O(n)。
常见问题 1、hashMap中的键为自定义的类型。放入 HashMap 后,我们在外部把某一个 key 的属性进行更改,然后我们再用这个 key 从 HashMap 里取出元素,这时候 HashMap 会返回什么?
答:
这个需要根据 自定义类型的 hash函数 和 equals函数 来定:
若 属性 会影响到 hash函数 或者 equals函数 的结果,则 返回的结果会变成 null。
若 属性 不影响到 hash函数 和 equals函数 的结果,则 返回的结果不变。
注:
equal 默认实现为 指针比较
hash 默认实现为 将内存地址经过特定算法转化而成的int值,具体实现有操作系统决定。
2、加载因子 loadFactor(默认0.75):为什么需要使用加载因子,为什么需要扩容呢
答:
如果loadFactor很大,空间利用率就会越高,但是碰撞的几率就会越来越高。
3、为什么需要红黑树
在一种极端情况下,多个 HashCode 的值 落在了同一个桶中,使 hashMap 变成了链表,查找时间从 O(1)到 O(n)。这样非常耗时。
它是如何工作的?
刚开始前面产生冲突的 那些KEY 对应的记录只是简单的追加到一个链表后面,这些记录只能通过遍历来进行查找。
Java HashMap工作原理及实现
https://www.cnblogs.com/yangming1996/p/7997468.html
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37356262/article/details/80543218
http://www.importnew.com/20386.html
http://www.importnew.com/28263.html