[TOC]
Servlet 运行在服务端的Java小程序,是sun公司提供一套规范(接口),用来处理客户端请求、响应给浏览器的动态资源。但servlet的实质就是java代码,通过java的API 动态的向客户端输出内容。
servlet 概述
Servlet是Java Web的三大组件(Servlet,Filter,Listener)之一,属于动态资源 ,运行在 Web 服务器或应用服务器上的程序作用为处理请求,服务器会把接收的请求交给Servlet来处理,在Servlet中通常需要:
接受请求数据、处理请求、完成响应
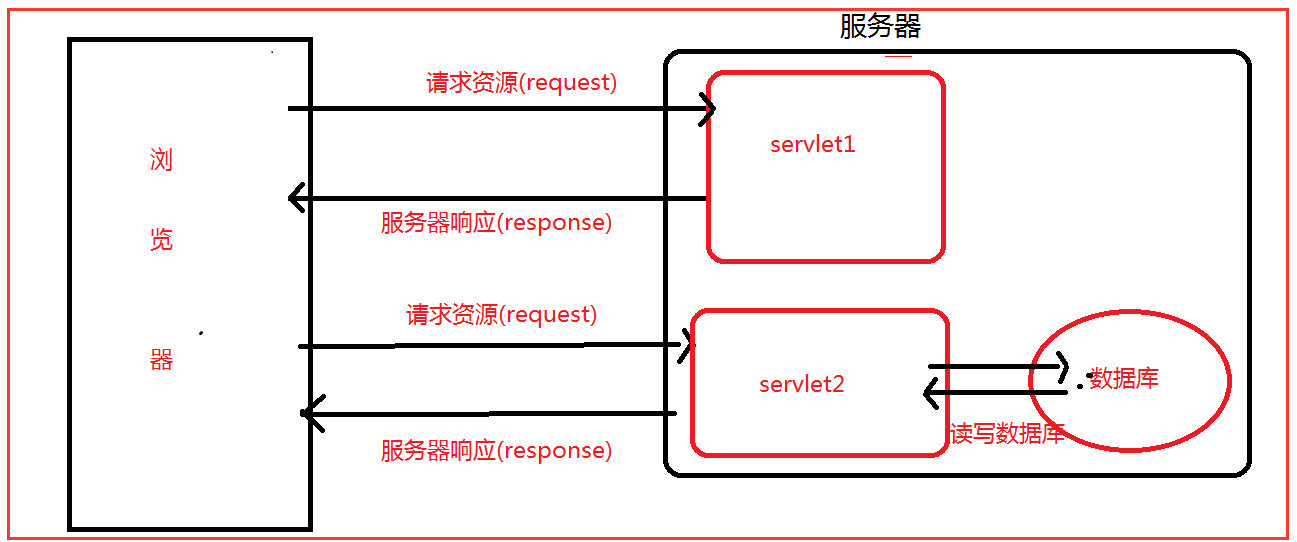
实现 servlet
- 实现javax.servlet.Servlet接口
- 继承javax.servlet.GenericServlet类
- 继承javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet类(用得较多)
例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class Servlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doPost()...");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doGet()...");
}
}
|
线程安全问题
由于一个 servlet 是一个实例对象,因此需要注意 servlet 的线程问题。
- 尽量不要在 servlet 中创建成员变量。
- 若实在需要,可以创建无状态成员 或者 只读成员
servlet 生命周期
创建实例:
- 第一次请求 servlet
- 启动时立即创建,即load-on-startup servlet
初始化:调用init()方法
响应请求:调用service()方法, 根据请求方法选择 doGet 或 doPost
实例销毁:调用destroy()方法,在servlet容器停止或者重新启动时发生
servlet调用图
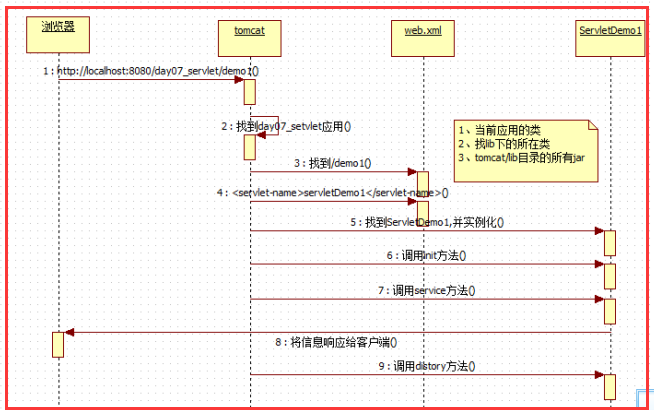
Servlet访问的过程:
Http请求—->web.xml——–> url -pattern—–>servlet-name—–>servlet-class—–> QuickStratServlet(对应的Class文件)
其他类介绍
ServletConfig
用于封装servlet的配置信息:
- ServletName: 当前Servlet在web.xml中配置的名字
- ServletContext: 当前web应用的ServletContext对象
- InitParameter: 当前Servlet指定名称的初始化参数的值
- InitParameterNames: 当前Servlet所有初始化参数的名字组成的枚举
ServletContext
WEB容器在启动时,它会为每个WEB应用程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表当前web应用。
不同 servlet 之间共享数据
由于一个WEB应用中的所有Servlet共享同一个ServletContext对象,因此Servlet对象之间可以通过ServletContext对象来实现通讯。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
context.setAttribute("name", "smyhvae");
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
class ServletB extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
String myName = (String) context.getAttribute("name");
System.out.println(myName);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
|
设置初始化参数
在web.xml中使用标签(与Servlet标签并列)为整个Web应用配置属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| public class ServletTest03 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
String value1 = context.getInitParameter("username");
String value2 = context.getInitParameter("password");
System.out.println(value1 + ";" + value2);
Enumeration enumeration = context.getInitParameterNames();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = (String) enumeration.nextElement();
String value = context.getInitParameter(name);
System.out.println(name + ";" + value);
}
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
|
转发
- 请求重定向: 302+Location(两次请求两次响应)
- 请求转发: 服务器内不进行资源流转 (一次请求一次响应,来实现资源流转)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class ServletTest04 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = this.getServletContext().getRequestDispatcher("/servlet/ServletTest05");
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
|
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangyinhua/p/7625851.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/p/4140877.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangyinhua/p/7629099.html

